India’s digital data market is projected to become the world’s largest, with over 600 million-plus active internet users, standing only next to China. It is forecasted that the data will become “new wealth” for developing the nation’s economy.
Did you know?
According to recent studies, the number of internet users in rural areas will soon increase by 30-40% in the next couple of years. Due to this rapid digital transformation there is a growing focus on data security threats, which can directly impact India’s economic development.
What is PDP bill 2019?
Key features of the Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019:
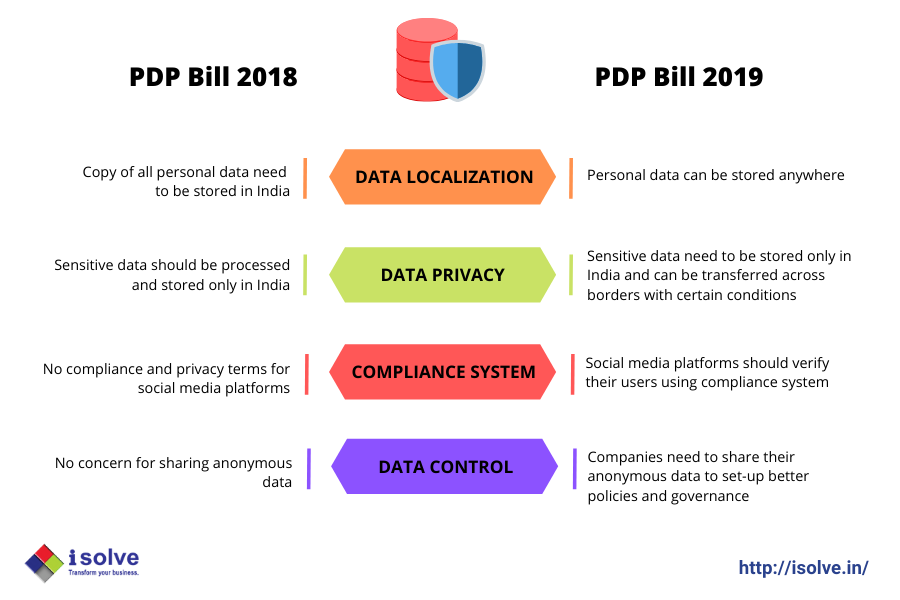
- Sensitive and critical personal data will be stored in local servers within the physical boundaries of the country.
- The free flow transfer of personal data outside the country can be conducted under certain conditions.
- Critical and sensitive data from financial and health sectors need to be collected, stored and processed only in India.
- Social Media platforms should implement a compliance system for verifying its users to control the spread of misinformation.
- The bill allows direct authority of the Government to check data fiduciaries of all organizations to control their anonymized data for setting up better policies and governance.
Major impact of PDP bill 2019 on tech companies having remote servers:
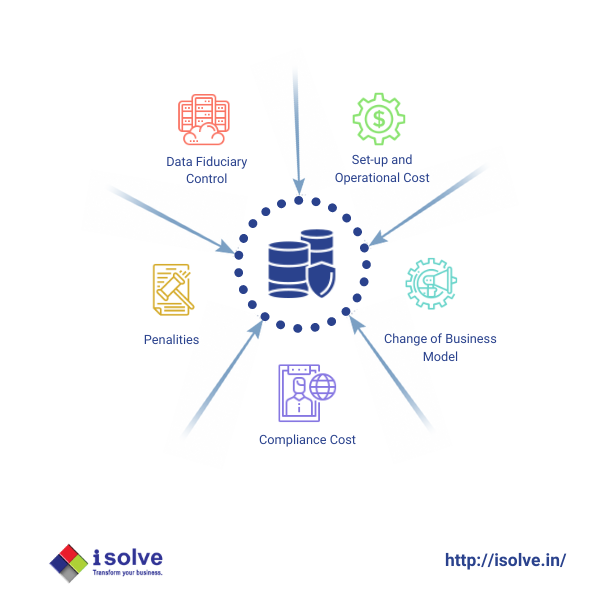
1.Penalties: The bill has included a penalty of 2- 5% of organization turn over, in case of transferring sensitive and critical data to their remote servers.
2.Data Fiduciary Control: The bill expresses the authority to control data fiduciaries and its anonymous data to protect the interest of data principal.
3.Change of Business Models: The introduction of this bill can make the tech companies with remote servers to alter their business operations/models to gain the ability to collaborate with other foreign companies and reduce their E-barrier.
4.Compliance Cost: The collection and processing of data by other foreign agencies will be disrupted and may hinder the process of business operations.
5.Setup and Operational Cost: Setting up local servers in India will be a big hurdle for foreign and existing tech companies operating in India.
It becomes extremely difficult for PDP non-compliant tech companies to provide data security and storage operations to other SME’s. Tech companies with remote servers has to set-up their data processing centers within the boundaries of India, which eventually increase their operational and tech cost.
At iSolve technologies, the data security and processing operations align with the privacy regulations suggested in the personal data protection bill. The collected data is processed and stored within the boundaries of India to ensure PDP compliance for our organization.
FAQS
Data Sovereignty is a term used to describe the data enforcement laws and governing structures of the nation where it is processed.
The service providers who collect, organize, store and structure the data of entities are called data fiduciaries. The process of data collection and storage is usually done at data processing centers.
Data localization is an enforcement law which restricts the free flow of data transfer across the borders and to stores and processes personal data within the country's boundaries.
1.What is Data Sovereignty ?
Data Sovereignty is a term used to describe the data enforcement laws and governing structures of the nation where it is processed.
2.What is Data Fiduciary?
The service providers who collect, organize, store and structure the data of entities are called data fiduciaries. The process of data collection and storage is usually done at data processing centers.